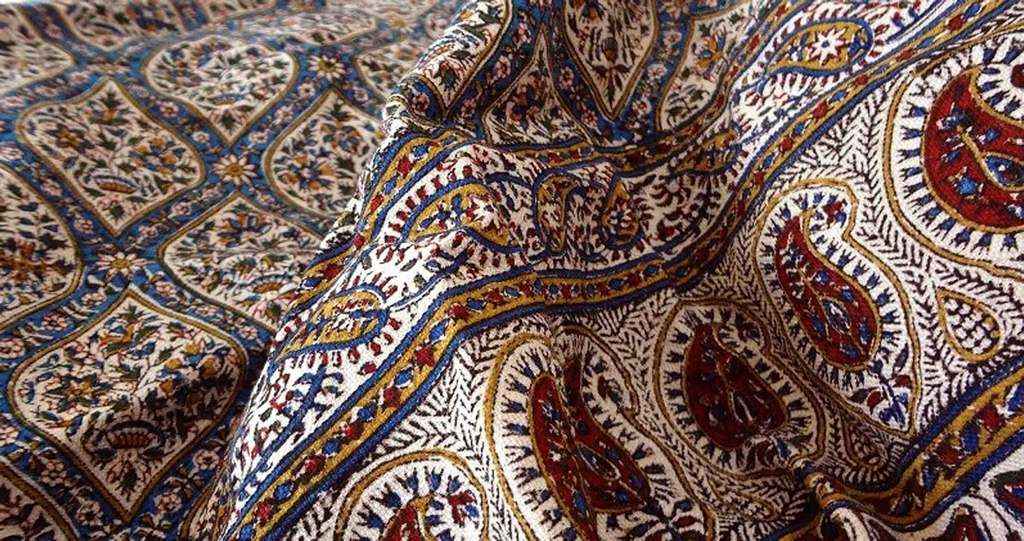
Khatamkari
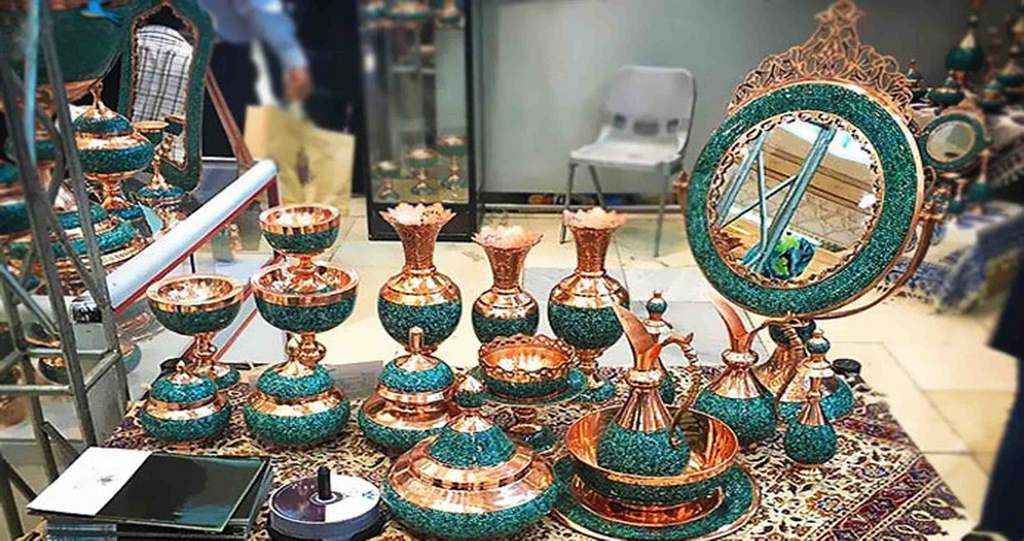
Khatamkari literally means decorating objects’ surfaces with small pieces like tiles and it is one of the Persian arts wherein the surface of wooden or metallic articles is decorated with pieces of wood, bone and metal cut in a variety of shapes and designs.

This art, to some extent, has existed in Iran from long ago. Inlaid articles in the Safavid era took on a special significance, as artists used this art on doors, windows, mirror frames, Qur’an boxes, pen and pen holders, lanterns and tombs.
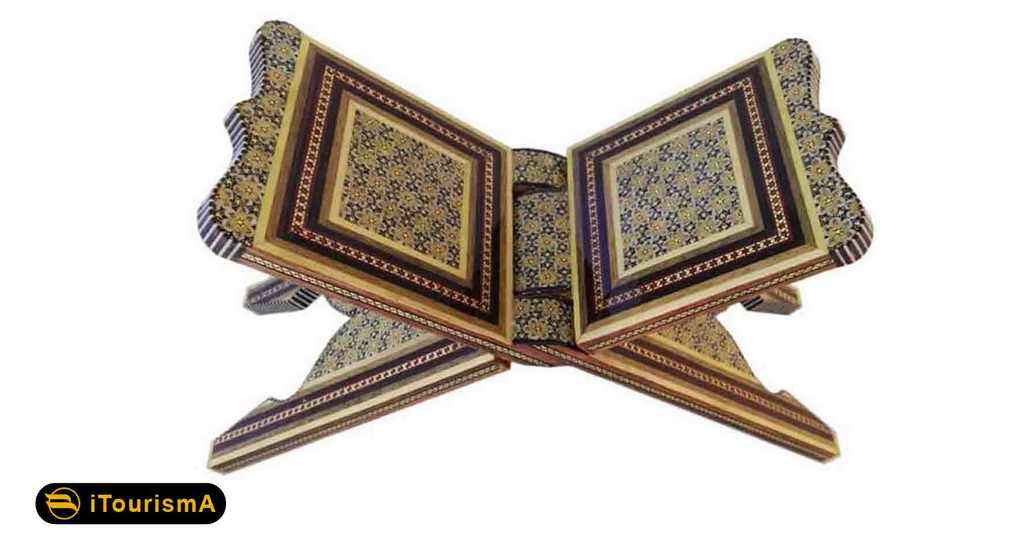

Also, in some royal buildings, doors and various items have been inlaid. The inlaid-ornamented rooms in Sa’dabad and Marble Palace in Tehran are among masterpieces of this art.

Incorporating techniques from China and improving it with Persian know-how, this craft existed for more than 700 years and is still practiced in Shiraz and Isfahan.
How to do it
Gold, silver and etc. can be used for collector coins. These rods are first assembled into triangular beams with geometric patterns, and then these are assembled again and glued into bundles in a strict order to form a cylinder of about 70cm, whose edge shows the unity of the base of the final decoration.

These cylinders are then sheared in shorter cylinders, then compressed and dried between two wooden plates, before undergoing a final cut that makes slices of about 1 mm in thickness. The latter are then ready to be plated and glued on the support object to be decorated before being lacquered. They can be preheated to soften them, if the object is curved, so that they can perfectly marry the curves. The decorated objects are: boxes, chess or backgammon, frames, or even musical instruments.

The Khatam technique can also be applied to the famous Persian miniatures, thus creating true works of art.